The human eye is a complex system that relies on numerous components working together. Just like any other part of the body, the eyes require proper nutrition to function optimally and maintain healthy vision.
Eye anatomy
The eye is composed of several interconnected structures, including the cornea, lens, retina and optic nerve. Light enters through the cornea and passes through the lens, focusing on the retina, where photoreceptor cells called rods and cones convert it into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted into the brain via the optic nerve, enabling us to see.
Essential nutrients for Eye Health
Vitamin A
Perhaps the most well-known nutrient for eye health is vitamin A. This fat-soluble vitamin is crucial for maintaining clear vision. A deficiency can lead to night blindness and other vision issues. Vitamin A is really important for its part in retina health and light sensitive cells. Foods high in vitamin A include sweet potatoes, carrots, spinach and liver.
Vitamin C
This is another really important antioxidant which plays a critical role in our bodies, including protecting the eyes from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. It is also protective of the blood vessels which supply blood to our eyes. Good sources of vitamin C include berries, citrus fruits and bell peppers.
Vitamin E
This is another antioxidant which is needed for its contribution towards eye health. It helps protect the cells in our eyes from damage and supports the overall health of the eye tissues. Foods high in vitamin E include nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils.
Zinc
Zinc is a mineral that is essential of maintaining eye health of the retina. It is involved in transporting Vitamin A from the liver to the retina, where it is needed for vision. Therefore, it is important to maintain good zinc levels. Good sources of Zinc include oysters, beef, chickpeas and pumpkin seeds.
Lutein and Zeaxanthin
These two carotenoids are found in high concentrations in the retina and are known for their protective role from harmful high energy light waves such as ultraviolet rays. They also play a role in an antioxidant capacity. Foods rich in these antioxidants include leafy green vegetables such as kale and spinach.
Omega 3
Omega 3 fatty acids, in particular, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), are important for maintaining the structure and function of the eyes cell membranes. Good sources of omega 3 include fatty fish such as salmon, walnuts and flaxseeds.
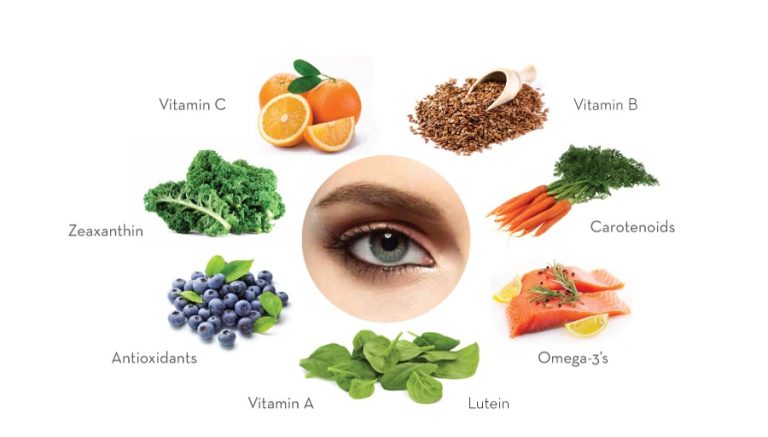

The Role of Antioxidants:
Antioxidants are compounds that help protect the body’s cells, including those in the eyes, from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells, including those in the eyes, and contribute to various eye conditions, including cataracts and age-related macular degeneration(AMD). Vitamins C and E, along with lutein and zeaxanthin, act as antioxidants in the eye. They help neutralize free radicals, reducing the risk of oxidative damage to the retina and other eye tissues. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables, which are abundant in these antioxidants, can help maintain eye health.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet:
While individual nutrients play an essential role in maintain eye health, it is crucial to emphasize the importance of a balance diet. The interactions between various nutrients can affect the absorption utilisation of another. Therefore, a well-rounded diet that includes a variety of foods is key to providing the eyes with all the essential nutrients.
Additionally, a maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet can also help prevent conditions like diabetes and hypertension which are risk factors for eye disease such as diabetic retinopathy and glaucoma.

Conditions Affecting Eye Health
Cataracts
Cataracts are a common age-related eye condition in which the lens if the eye becomes cloudy, leading to blurred vision. Research suggests that antioxidants like vitamin C and E may help to reduce the
risks of cataracts developing.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
AMD is a progressive eye disease that affects the macula, a part of the retina that is responsible for
central vision. Lutein, zeaxanthin and omega 3 fatty acids have been linked to a reduced risk of AMD, making them essential for long-term eye health.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions characterized by increased intraocular pressure, which can damage the optic nerve and lead to vision loss. Whilst nutrients alone cannot completely prevent or cure glaucoma, they may contribute to the overall health of the eye. Overall, the role of nutrients in maintaining eye health cannot be overlooked.
A diet rich in vitamins A, C and E, Zinc, lutein, zeaxanthin and omega 3 fatty acids can help protect the eyes from damage and reduce the risk of developing these eye conditions. Antioxidants play a vital role in preserving the health of the retina and other eye tissues by neutralising the free radicals.
It is also important to remember that no single nutrient can work in isolation. A balanced diet that includes a verity of nutrient rich foods is the most effective in supporting and maintaining eye health.
Our Eye Health Fix Picks